Welcome to an insightful article that aims to provide you with effective solutions for resolving Windows Stop Code Errors. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore practical strategies to tackle these frustrating issues head-on, empowering you to overcome them and optimize your Windows experience. Whether you are a tech-savvy individual or a beginner, this article has got you covered with user-friendly tips and tricks. So, let’s dive into the world of troubleshooting and bid farewell to those pesky Stop Code Errors on your Windows device.
Understanding Windows Stop Codes
To resolve Windows Stop Code errors effectively, follow these steps:
1. Identify the Stop Code: Read the error message on the Blue Screen carefully. It will contain a specific Stop Code, such as “0xc000021a” or “MEMORY_MANAGEMENT.”
2. Research the Stop Code: Use Microsoft’s resources to search for the meaning and possible causes of the Stop Code. Visit the Microsoft website or use the Blue Screen Troubleshooter tool for detailed information.
3. Take appropriate action: Once you understand the cause of the error, follow the recommended steps to resolve it. This may involve updating drivers, performing system scans, or repairing the registry.
Remember to regularly update your Windows 10 operating system and drivers to minimize the chances of encountering Stop Code errors. If you need further assistance, reach out to Microsoft’s support team or consult online forums for additional guidance.
Common Windows 10 Stop Codes
- CRITICAL_PROCESS_DIED: This stop code indicates that a critical system process has unexpectedly terminated.
- SYSTEM_SERVICE_EXCEPTION: This stop code is usually caused by a faulty driver or system service that is not functioning properly.
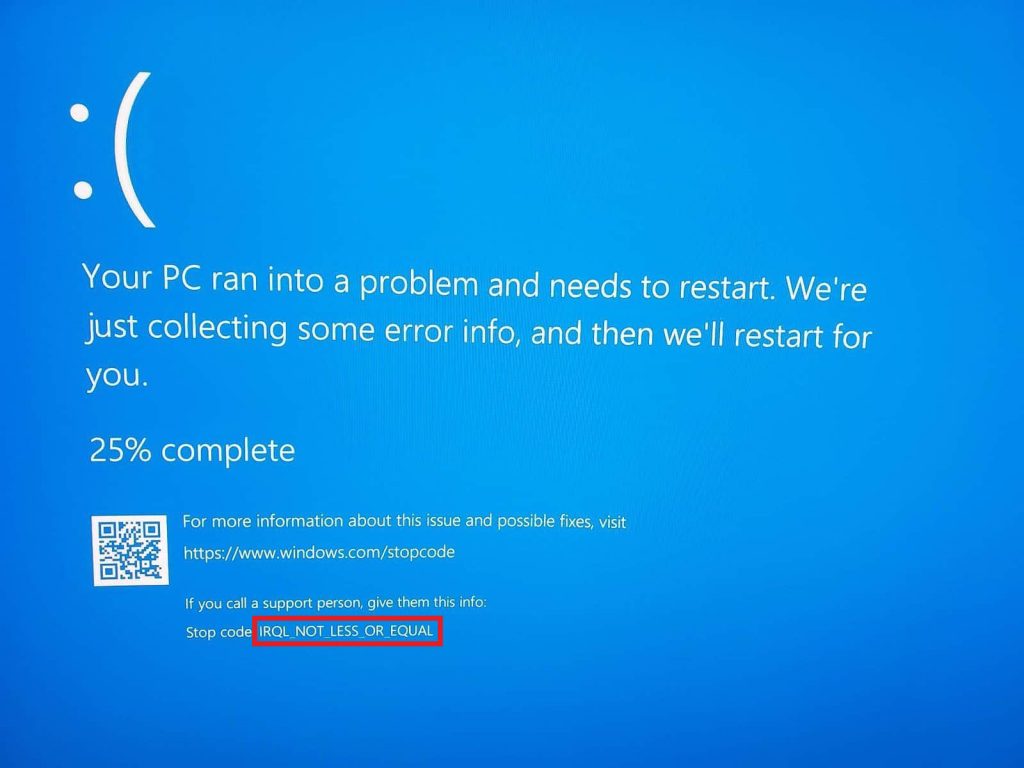
- IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL: This stop code typically occurs when a driver or kernel-mode process attempts to access a memory address without proper permissions.
- PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA: This stop code indicates that the system attempted to access a nonexistent or invalid memory address.
- KERNEL_SECURITY_CHECK_FAILURE: This stop code suggests that a violation was detected in the kernel’s handling of security features.
- SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED: This stop code occurs when a thread within the operating system encounters an unhandled exception.
- DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL: This stop code is similar to IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL, but it specifically implicates a faulty or incompatible driver.
- UNEXPECTED_STORE_EXCEPTION: This stop code arises when the system encounters data corruption in its memory store.
- SYSTEM_SERVICE_EXCEPTION: This stop code typically occurs when a faulty driver or system service fails to execute properly.
- INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE: This stop code appears when Windows is unable to access the boot device due to a misconfiguration or hardware issue.
Finding Windows 10 Stop Codes on Your PC
Resolving Windows Stop Code Errors Effectively
If you’re experiencing screen errors on your PC and receiving Windows 10 Stop Codes, don’t panic. Here’s how you can find and resolve these issues.
1. When your PC crashes, take note of the Stop Code message displayed on the screen. This message can provide valuable information about the problem.
2. Start your PC in Safe Mode by pressing the F8 key repeatedly during startup. This will help you troubleshoot and identify any software or driver-related issues.
3. Use the Blue Screen Troubleshooter to automatically diagnose and fix common blue screen errors.
4. Check for any recent updates or changes to your hardware or software. Sometimes, incompatible updates or installations can cause these errors.
5. If you’re still having trouble, consider seeking help from professional IT support or the Microsoft community.
Remember, resolving Windows Stop Code errors requires patience and attention to detail. By following these steps, you’ll be on your way to resolving these issues effectively.
Analyzing Windows Logs and Diagnostic Tools
When encountering Windows Stop Code Errors, it is crucial to analyze Windows logs and utilize diagnostic tools for effective resolution. These tools provide valuable insights into the underlying issues causing the errors on your computer.
To begin, access the Windows logs by following these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type “eventvwr.msc” and press Enter.
3. In the Event Viewer window, navigate to “Windows Logs” and select “System” or “Application” logs.
Next, use diagnostic tools such as the Windows Memory Diagnostic or the BSOD Screen Viewer to identify the root cause of the error. These tools provide detailed information about the error, including the error code and the faulty component.
By analyzing the logs and using diagnostic tools, you can troubleshoot and resolve Windows Stop Code Errors more effectively, ensuring a smoother and more stable computing experience. Remember to seek further assistance through Microsoft support or online forums if needed.
Fixing Windows Stop Codes: Basic Steps
- Restart your computer:
- Click on the Start button.
- Select the Power option.
- Choose Restart from the drop-down menu.
- Check for Windows updates:
- Press the Windows key and type Windows Update.
- Select Windows Update settings from the search results.
- Click on Check for updates.
- If updates are available, click on Install now.
- Scan for malware:
- Open your antivirus software.
- Initiate a full system scan.
- If any malware is detected, follow the software’s instructions to remove it.
- Check for hardware issues:
- Ensure all hardware components are properly connected.
- Check for any loose cables or connections.
- If possible, test the hardware on a different computer to identify any faulty components.
- Update device drivers:
- Press the Windows key and type Device Manager.
- Select Device Manager from the search results.
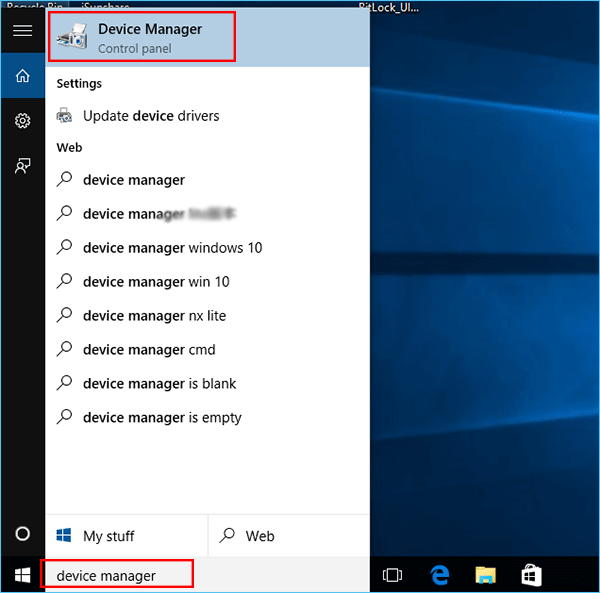
- Expand the categories and right-click on the device.
- Choose Update driver and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Run a memory diagnostic:
- Press the Windows key and type Windows Memory Diagnostic.
- Select Windows Memory Diagnostic from the search results.
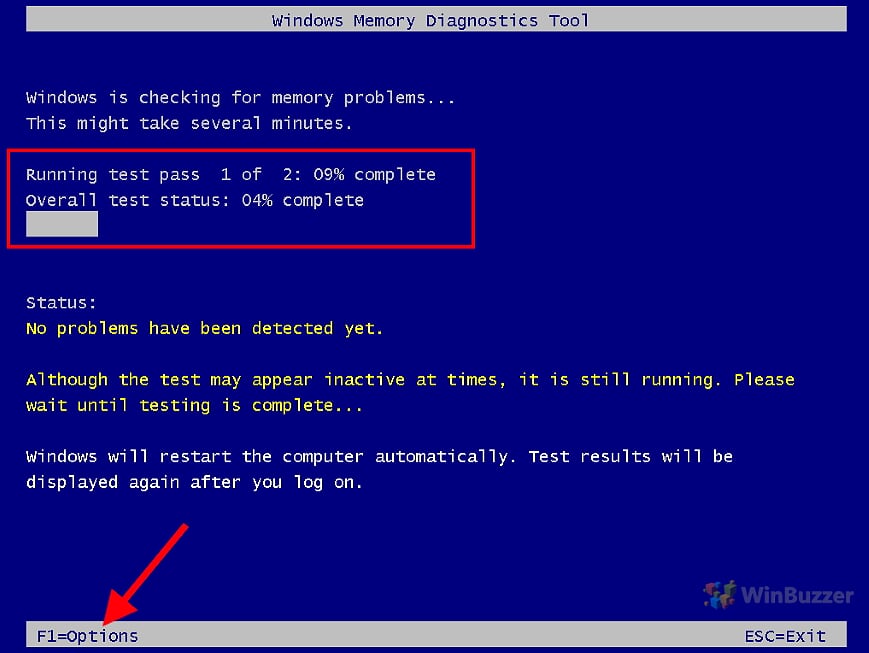
- Click on Restart now and check for problems.
- Wait for the diagnostic to complete and follow any recommended actions.
Restarting and Checking System Utilities
If you are experiencing Windows Stop Code errors, it can be helpful to restart and check your system utilities. Follow these steps to effectively resolve the issue:
1. Restart your computer: Sometimes a simple restart can fix common system errors.
2. Check for software conflicts: Uninstall any recently installed apps or programs that may be causing the issue.
3. Update your drivers: Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to Stop Code errors. Visit the manufacturer’s website to download and install the latest drivers for your hardware.
4. Run a memory diagnostic: Use the built-in Windows Memory Diagnostic tool to check for any memory-related issues.
5. Scan for malware: Use a reputable antivirus program to scan your system for any malicious software that may be causing the errors.
If you continue to experience issues, it may be necessary to seek further assistance from Microsoft Support or consult online resources for more specific troubleshooting steps. Remember to provide as much information as possible about the error, including the Stop Code and any error messages you encounter.
Updating and Uninstalling Incompatible Software
To resolve Windows Stop Code Errors effectively, it is important to update or uninstall any incompatible software on your system.
First, identify the software causing the problem by checking for error messages or examining the event logs. Once you have identified the software, follow these steps:
1. Update the software: Check the software developer’s website for any available updates or patches. Download and install them to ensure compatibility with your Windows system.
2. Uninstall the software: If updating the software doesn’t resolve the issue, consider uninstalling it. Go to “Control Panel” and select “Programs and Features” or “Apps and Features.” Find the problematic software in the list and click “Uninstall.”
3. Restart your computer: After updating or uninstalling the software, restart your computer to apply the changes.
By updating or uninstalling incompatible software, you can eliminate potential conflicts and resolve Windows Stop Code Errors.
For more detailed instructions or if you encounter any trouble, consult Microsoft’s support documentation or reach out to their dedicated support team for further assistance.
Protecting Your Data during Windows Stop Codes
1. Back up your data regularly to prevent loss in case of a Windows Stop Code error.
2. Use a reliable antivirus software to protect your system from malware that can cause these errors.
3. Keep your Windows operating system up to date with the latest security patches and updates.
4. If you encounter a Windows Stop Code error, take note of the error message and any relevant information.
5. Use the error message to search for solutions online or consult Microsoft’s support resources for troubleshooting steps.
6. Avoid making any changes to your system without proper guidance, as this can worsen the error or cause data loss.
7. If you suspect hardware issues, such as faulty memory or hard drive, consider seeking professional help for repairs.
8. Remember to regularly save your work and close any open applications to minimize potential data loss during a Windows Stop Code error.
Stay proactive in protecting your data and resolving Windows Stop Code errors effectively.
