Welcome to our guide on starting Windows 10 in Safe Mode! In this article, we will explore nine different methods to help you access Safe Mode quickly and efficiently. Whether you’re troubleshooting issues or simply looking to perform system maintenance, we’ve got you covered with these easy-to-follow steps. Let’s dive in and discover the various ways to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode!
Symptoms and Resolution
SYMPTOMS AND RESOLUTION:
If you’re experiencing issues with your Windows 10 operating system, starting your computer in Safe Mode can help troubleshoot and resolve the problem. Here are 9 ways to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode:
1. Using the Start Menu:
– Click on the Start menu, then hold the Shift key and click Restart.
– Select Troubleshoot, then Advanced options, and finally Startup Settings.
– Click Restart, and then choose Safe Mode from the list.
2. Using the Settings App:
– Press Windows key + I to open the Settings app.
– Go to Update & Security, then Recovery.
– Under Advanced startup, click Restart now.
– Follow the same steps as in method 1 to enter Safe Mode.
3. Using the Sign-in screen:
– Hold the Shift key and click the Power button on the sign-in screen.
– Select Restart, then follow the same steps as in method 1.
4. Using the Command Prompt:
– Press Windows key + X and select Command Prompt (Admin).
– Type bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal and press Enter.
– Restart your computer, and it will boot into Safe Mode.
5. Using the System Configuration tool:
– Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
– Type msconfig and press Enter.
– In the System Configuration window, go to the Boot tab.
– Check the Safe boot box and click OK.
– Restart your computer to enter Safe Mode.
6. Using a Windows Installer USB:
– Create a Windows Installer USB flash drive using the Media Creation Tool.
– Boot your computer from the USB drive.
– Select your language preferences and click Next.
– Choose Repair your computer, then Troubleshoot, and finally Advanced options.
– Select Startup Settings, then click Restart.
– Follow the same steps as in method 1.
7. Using a System Restore Point:
– Press Windows key + R, then type rstrui.exe and press Enter.
– Click Next, then select a restore point before the issue occurred.
– Follow the on-screen instructions to restore your computer to that point.
8. Using Automatic Repair:
– Insert a Windows Installer USB or DVD into your computer.
– Boot your computer from the USB or DVD.
– Select your language preferences and click Next.
– Choose Repair your computer, then Troubleshoot, and finally Advanced options.
– Select Startup Repair, and let the tool fix any startup issues.
9. Using the Windows Preinstallation Environment (Windows PE):
– Boot your computer using a Windows PE USB or DVD.
– Select your language preferences and click Next.
– Choose Repair your computer, then Troubleshoot, and finally Advanced options.
– Select Command Prompt.
– Type bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal and press Enter.
– Restart your computer to enter Safe Mode.
Starting Windows 10 in Safe Mode can help diagnose and resolve various issues with your computer, such as software conflicts or driver problems. It allows you to start your computer with only essential services and drivers, making it easier to troubleshoot and fix the problem. Use the methods above based on your preference and situation to enter Safe Mode and resolve any issues you may be experiencing.
Boot into Safe Mode from Windows 11 or Windows 10
To start Windows 11 or Windows 10 in Safe Mode, follow these steps:
1. Click the “Start” button on the desktop or press the Windows key on your keyboard.
2. Type “Settings” in the search bar and open the Settings app from the results.
3. In the Settings app, click on “Update & Security” and then select “Recovery” from the left-hand menu.
4. Under “Advanced startup,” click on the “Restart now” button.
5. Your computer will restart and display the Windows Recovery Environment.
6. In the Windows Recovery Environment, click on “Troubleshoot” and then choose “Advanced options.”
7. Select “Startup Settings” and click on the “Restart” button.
8. After your computer restarts, a list of startup settings will appear. Press the “4” key on your keyboard to enter Safe Mode.
9. Windows will now start in Safe Mode, allowing you to troubleshoot any issues you may be experiencing.
Remember to restart your computer in normal mode when you’re done troubleshooting.
python
import wmi
def enable_safe_mode():
c = wmi.WMI()
boot_config = c.Win32_ComputerSystem()[0].ModifyBootConfiguration(SafeMode=1, SafeBoot=1)
if boot_config[0] == 0:
print("Successfully enabled Safe Mode.")
else:
print("Failed to enable Safe Mode.")
def disable_safe_mode():
c = wmi.WMI()
boot_config = c.Win32_ComputerSystem()[0].ModifyBootConfiguration(SafeMode=0, SafeBoot=0)
if boot_config[0] == 0:
print("Successfully disabled Safe Mode.")
else:
print("Failed to disable Safe Mode.")
# Usage:
# enable_safe_mode() # Enable Safe Mode
# disable_safe_mode() # Disable Safe Mode
This code uses the `wmi` module to interact with the Windows Management Instrumentation to modify the boot configuration and enable or disable Safe Mode. You can uncomment the respective function calls to enable or disable Safe Mode as per your requirements.
Please note that this code snippet assumes you have already installed the `wmi` module. If not, you can install it using `pip install wmi`. Additionally, this code should be run with administrative privileges to make changes to the boot configuration.
Remember to exercise caution when modifying the boot configuration, as any incorrect changes can impact the system’s behavior.
Boot into Safe Mode from the sign-in screen in Windows 11 or Windows 10
To boot into Safe Mode from the sign-in screen in Windows 11 or Windows 10, you have several options:
1. Hold down the Shift key while selecting Restart from the Power menu.
2. Press the Windows key + X, then choose Settings. In Settings, go to Update & Security > Recovery. Under Advanced startup, select Restart now.
3. If you’re already signed in, press Ctrl + Alt + Delete, then click the Power button in the bottom-right corner. Hold down the Shift key while selecting Restart.
4. If you have a Windows installation media (USB flash drive or DVD), insert it and restart your computer. Choose your language preferences, then click Next. Select Repair your computer > Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings > Restart. Press F4 to enter Safe Mode.
5. If you’re using a Dell computer, press F8 repeatedly during startup until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears. Use the arrow keys to select Safe Mode and press Enter.
Remember, Safe Mode is a troubleshooting mode that loads only essential drivers and services. It can help diagnose and fix issues with your computer.
Boot into Safe Mode from outside of Windows 11 or Windows 10
To boot into Safe Mode from outside of Windows 11 or Windows 10, there are several methods you can try:
1. Use the Shift + Restart method: Hold down the Shift key and click on Restart from the Start menu. This will bring up the Advanced Startup Options menu.
2. Use the system configuration tool: Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box, then type “msconfig” and hit Enter. In the System Configuration window, go to the Boot tab and check the “Safe boot” option.
3. Use the Settings app: Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings app, then go to Update & Security > Recovery. Under the Advanced startup section, click on Restart now. Once in the Advanced Startup Options menu, choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, then click Restart. Press the F4 key to boot into Safe Mode.
4. Use the installation media: If you have a Windows installation disc or USB drive, insert it into your computer and boot from it. Select your language preferences, then click on “Repair your computer” > Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and finally click Restart. Press the F4 key to enter Safe Mode.
5. Use the Command Prompt: Boot into the Windows Recovery Environment by following method 4. Once in the Advanced Startup Options menu, choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Command Prompt. In the Command Prompt window, type “bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal” and hit Enter. Restart your computer to enter Safe Mode.
6. Use the Recovery Drive: If you have created a recovery drive, insert it into your computer and boot from it. Choose your keyboard layout, then select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings. Click Restart, and press the F4 key to boot into Safe Mode.
7. Use the “Automatic Repair” feature: If your computer fails to start normally multiple times, it will automatically enter the Automatic Repair mode. Wait for the “Preparing Automatic Repair” screen to appear, then select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings. Click Restart, and press the F4 key to enter Safe Mode.
8. Use the Advanced Boot Options menu: Restart your computer and press the F8 key repeatedly before the Windows logo appears. This will bring up the Advanced Boot Options menu. Use the arrow keys to select Safe Mode, then press Enter.
9. Use the Command Prompt in Windows Preinstallation Environment (Windows PE): Boot your computer using a Windows PE bootable USB drive or DVD. Once in Windows PE, open the Command Prompt and type “bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal” and hit Enter. Restart your computer to enter Safe Mode.
Remember, Safe Mode is a troubleshooting tool that loads a minimal set of drivers and services, so certain features may not be available. It can be helpful for troubleshooting issues related to software conflicts, device drivers, or malware.
Repair Your Computer
Starting Windows 10 in Safe Mode can help troubleshoot and fix various issues on your computer. Here are 9 ways to do it:
1. Use the Shift + Restart method: Press and hold the Shift key while selecting Restart from the Windows Start menu. Choose Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and then select Safe Mode.
2. Utilize the System Configuration tool: Press the Windows key + R, type “msconfig” and hit Enter. In the System Configuration window, go to the Boot tab and check the “Safe boot” box. Click OK and restart your computer.
3. Access the Settings app: Press the Windows key + I, select Update & Security, and then choose Recovery. Under Advanced startup, click Restart now. In the Choose an option screen, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and select Safe Mode.
4. Use the Command Prompt: Press the Windows key + X and choose Command Prompt (Admin). In the Command Prompt window, type “bcdedit /set {default} safeboot minimal” and hit Enter. Restart your computer to enter Safe Mode.
5. Enable Safe Mode through the sign-in screen: On the sign-in screen, hold the Shift key while selecting the Power icon, and click Restart. Follow the path Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and choose Safe Mode.
6. Boot from a Windows 10 installation media: Insert the installation media, restart your computer, and boot from the media. Select your language preferences, click Next, and choose Repair your computer. Navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and select Safe Mode.
7. Use the F8 or Shift + F8 method: During the boot process, repeatedly press the F8 key or Shift + F8 until the Advanced Boot Options menu appears. From there, select Safe Mode.
8. Access Safe Mode from the Settings app in Normal Mode: Press the Windows key + I, select Update & Security, and click Recovery. Under Advanced startup, click Restart now. In the Choose an option screen, go to Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and choose Restart. When your computer restarts, select Safe Mode.
9. Use the Windows Recovery Environment: Restart your computer and repeatedly press the F11 key to enter the Windows Recovery Environment. Select Troubleshoot > Advanced options > Startup Settings, and choose Restart. From there, select Safe Mode.
Remember that Safe Mode only loads essential drivers and services, so some features may be limited. Use Safe Mode to diagnose and resolve issues with your Windows 10 computer effectively.
Additional Information
- Safe Mode: Learn how to start Windows 10 in Safe Mode
- Multiple Ways: Discover 9 different methods to initiate Safe Mode
- System Configuration: Utilize the System Configuration tool to access Safe Mode
- Shift + Restart: Combine the Shift key and Restart option for quick Safe Mode entry
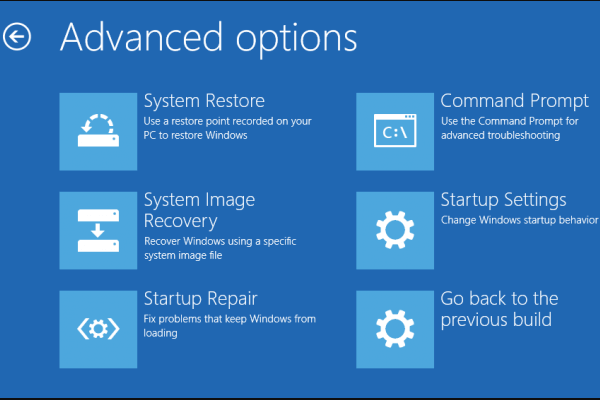
- Advanced Startup Options: Explore the Advanced Startup Options menu to enable Safe Mode
- Start Menu: Access Safe Mode via the Start Menu and relevant settings
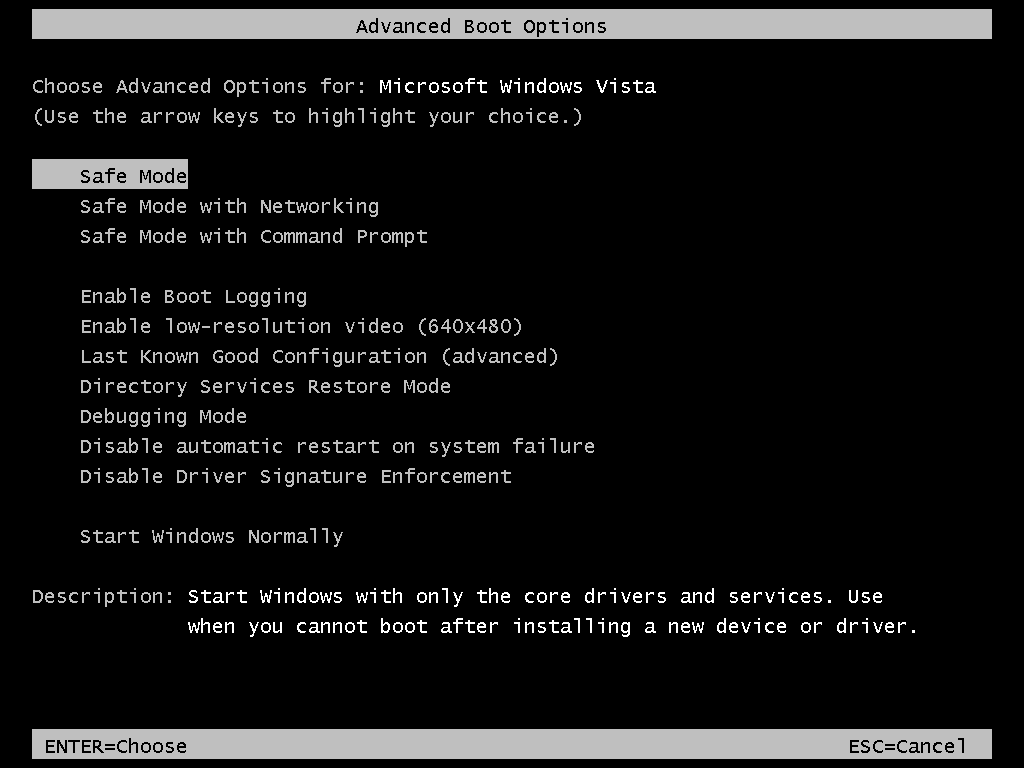
- Recovery Drive: Create or use a recovery drive to boot into Safe Mode
- Windows Settings: Access Safe Mode through the Windows Settings application
- Command Prompt: Utilize Command Prompt to initiate Safe Mode
