Unraveling the enigma of DPC Watchdog Violation Error on Windows 10/11: 11 ingenious solutions.
Understanding DPC Watchdog Violation
11 Ways to Fix DPC Watchdog Violation Error – Windows 10/11
1. Update Device Drivers: Use Device Manager to check for outdated or incompatible drivers. Update them manually or use a reliable driver update tool.
2. Check for Hardware Issues: Run hardware diagnostics to identify any faulty components. Replace or repair them if necessary.
3. Verify Disk Errors: Use the built-in Repair Disk Errors tool to scan and fix any disk-related issues that may be causing the error.
4. Adjust Timeout Values: Modify the timeout values of your system’s components to resolve timing conflicts that trigger the Watchdog Violation error.
5. Scan for System File Corruption: Run the System File Checker tool to scan and repair any corrupted or missing system files.
6. Disable SATA AHCI Controller Driver: If you recently installed a new driver, try disabling the SATA AHCI controller driver to see if it resolves the issue.
7. Remove Recently Installed Software/Drivers: Uninstall any recently installed software or drivers that may be causing conflicts with your system.
8. Check for Overclocking: If your computer is overclocked, revert it to its default settings and check if the error persists.
9. Update BIOS: Visit your computer manufacturer’s website and download the latest BIOS update for your model. Follow the instructions to install it.
10. Perform a Clean Boot: Temporarily disable all non-essential startup programs and services to identify any software conflicts.
11. Seek Professional Help: If none of the above methods resolve the issue, consider contacting a professional or Microsoft support for further assistance.
Remember to always backup your important files before attempting any fixes or changes.
Common Causes of DPC Watchdog Violation Error
-
Check for hardware issues:
- Ensure all hardware components are properly connected.
- Check for any loose connections or faulty hardware.

- Run hardware diagnostics to identify any potential issues.
-
Update drivers:
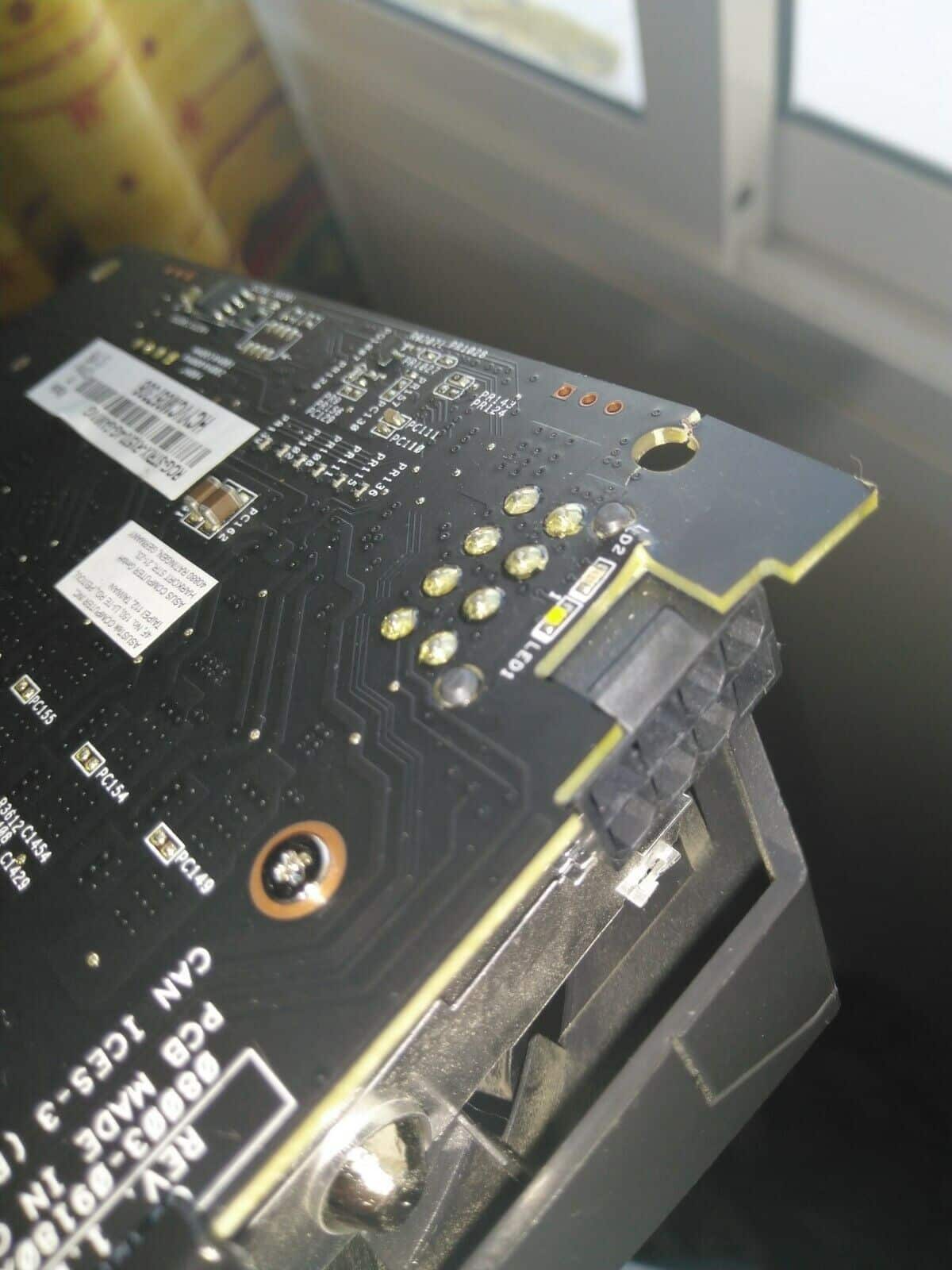
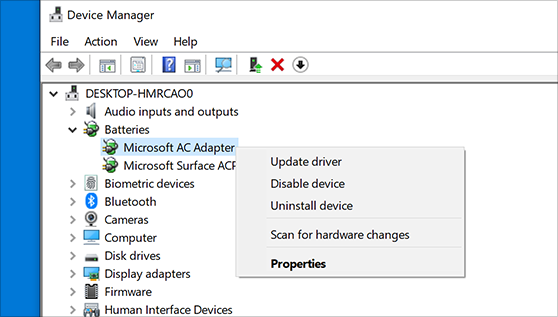
- Open Device Manager by pressing Win+X and selecting Device Manager.
- Locate the device with a yellow exclamation mark indicating a driver issue.
- Right-click on the device and choose Update driver.
- Select Search automatically for updated driver software and follow the on-screen instructions.
-
Scan for malware:
- Open your preferred antivirus software.
- Perform a full system scan to detect and remove any malware.
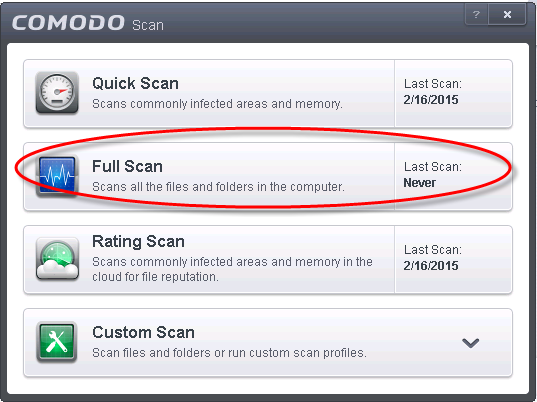
- If necessary, use a reputable malware removal tool to clean your system.
-
Update Windows:
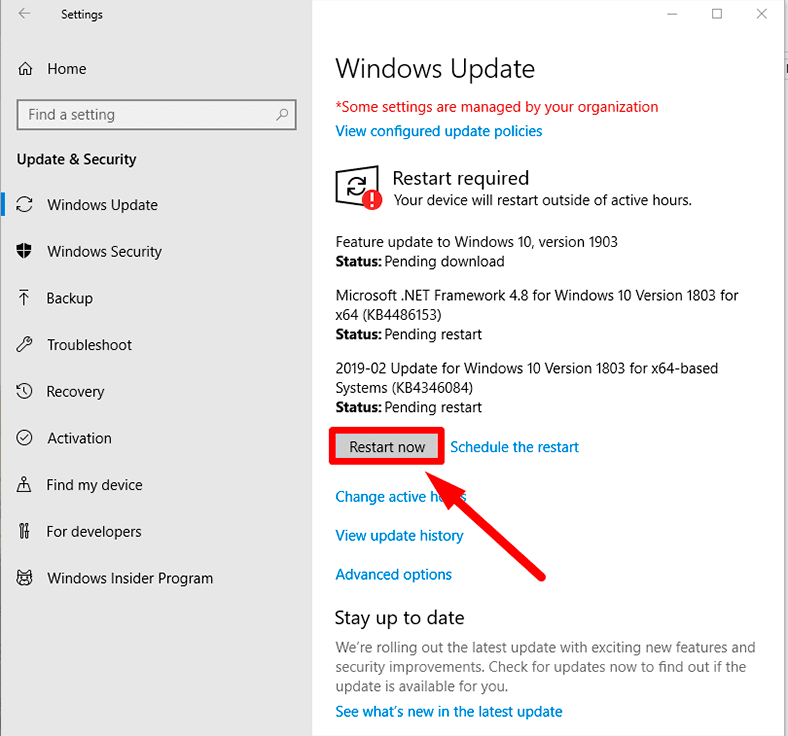
- Open Settings by pressing Win+I.
- Select Update & Security.
- Click on Check for updates and install any available updates.
- Restart your computer to apply the updates.
-
Disable overclocking:
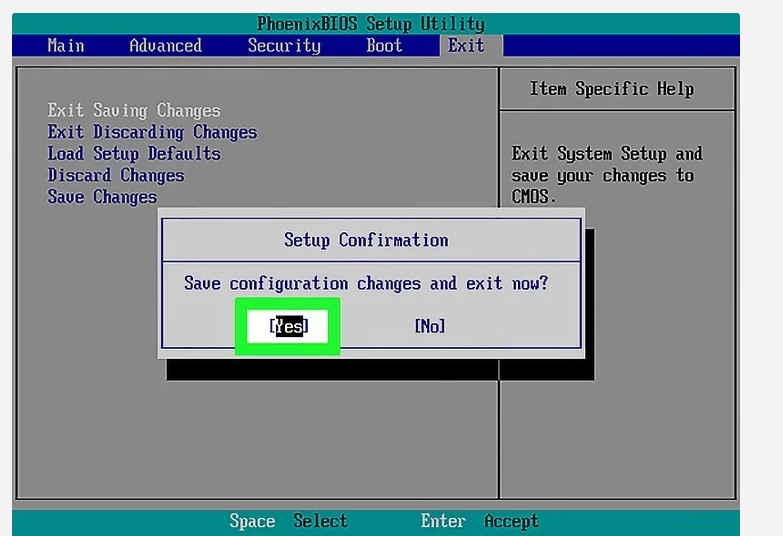
- Enter your computer’s BIOS or UEFI settings during boot.
- Locate the overclocking settings.
- Disable any overclocking options or revert to default settings.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI settings.
-
Check and repair corrupted system files:
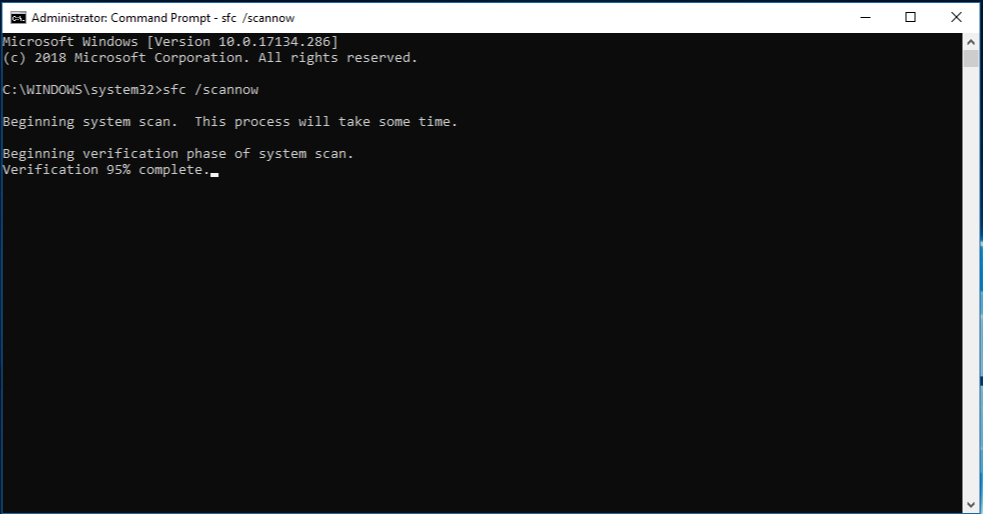
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator by pressing Win+X and selecting Command Prompt (Admin).
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
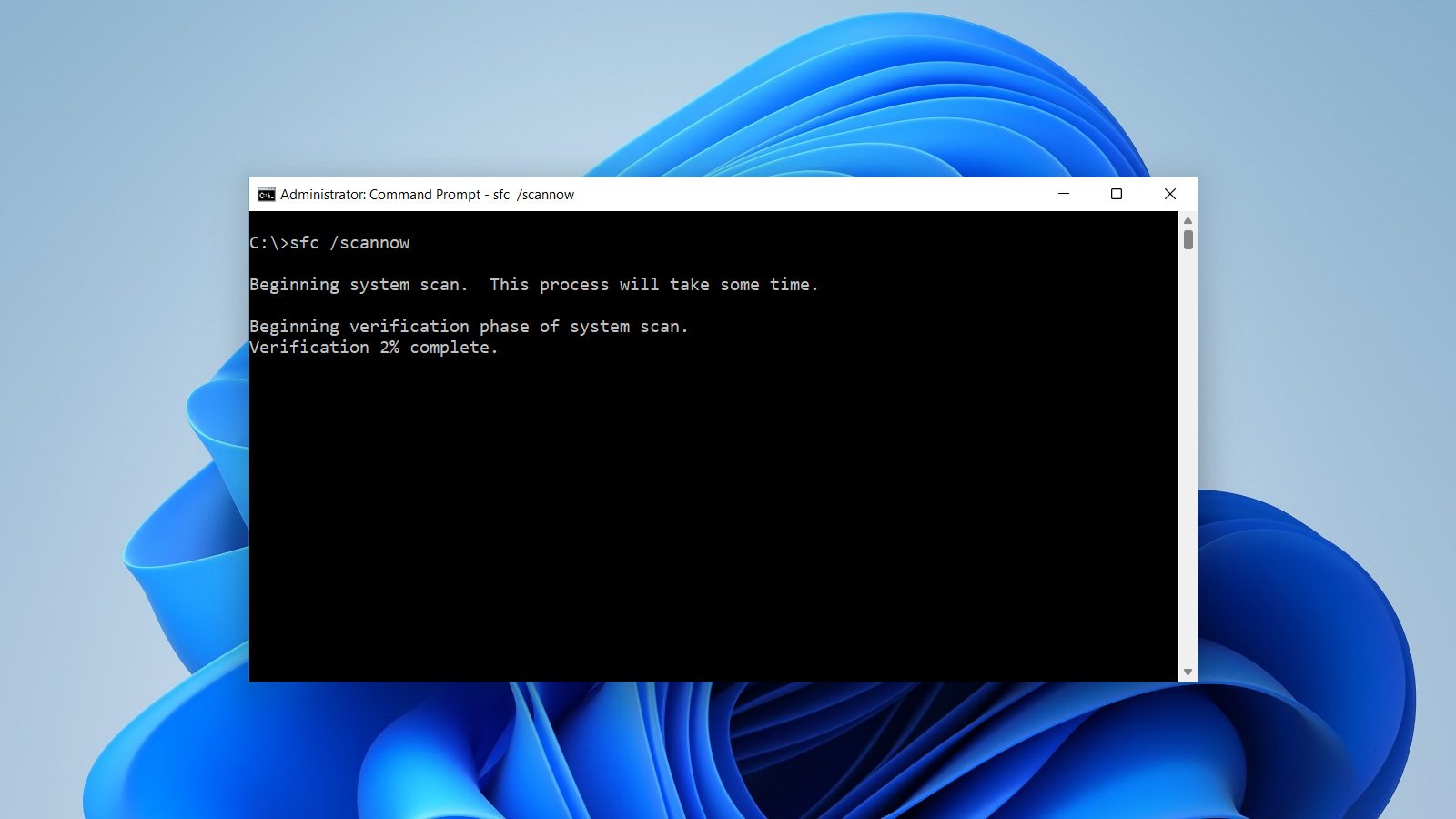
- Wait for the system file checker to scan and repair any corrupted files.
- Restart your computer after the process completes.
-
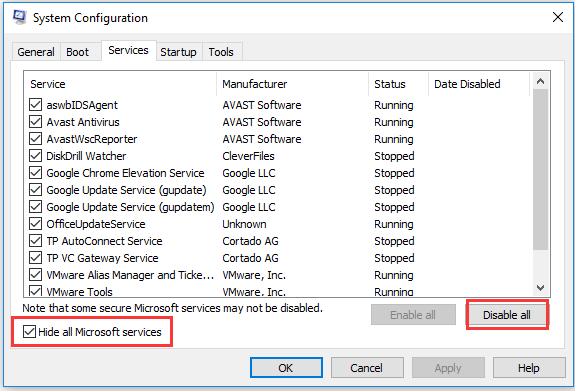
Disable unnecessary startup programs:
- Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Go to the Startup tab.
- Select the unnecessary programs and click on Disable.
- Restart your computer for the changes to take effect.
-
Update BIOS:
- Visit your computer manufacturer’s website and locate the support section.
- Find the latest BIOS update for your specific model.
- Download and follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer to update your BIOS.
- Exercise caution during the BIOS update process to avoid any interruptions.
-
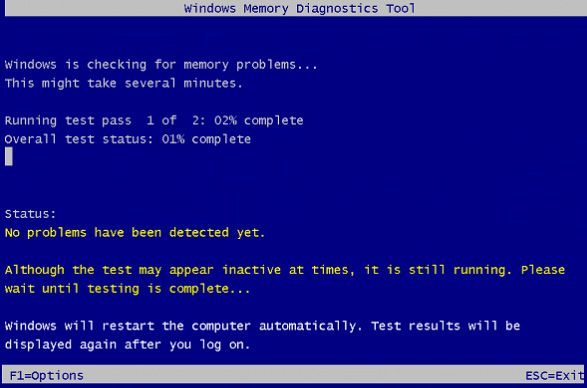
Check for faulty RAM:
- Open Windows Memory Diagnostic by pressing Win+R, typing mdsched.exe, and pressing Enter.
- Select Restart now and check for problems (recommended).
- Wait for your computer to restart and perform a comprehensive RAM test.
- Note any errors or issues reported by the diagnostic tool.
-
Reinstall Windows:
- Backup your important files and data to an external storage device.
- Access the Settings menu and select Update & Security.
- Choose Recovery and click on Get started under Reset this PC.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to initiate the reinstallation process.
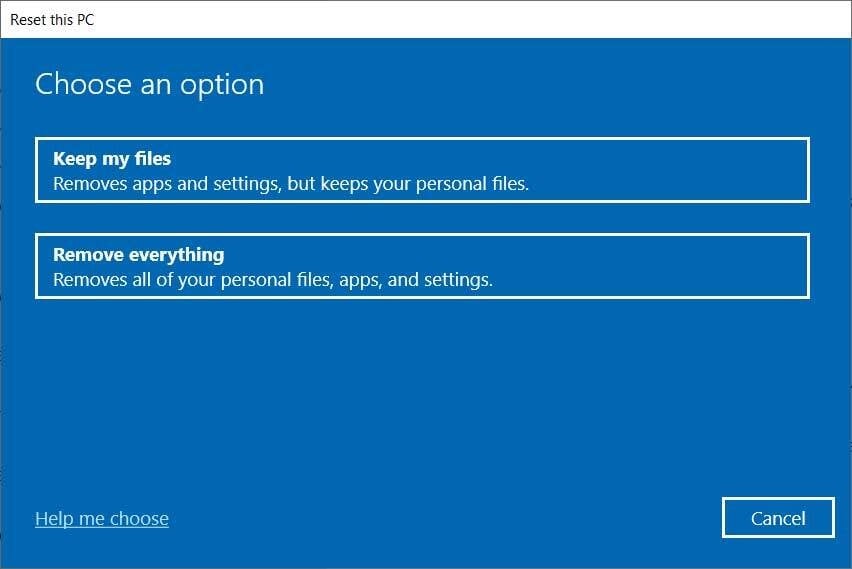
- Restore your files from the backup after completing the reinstallation.
-
Seek professional assistance:
- If none of the above steps resolve the DPC Watchdog Violation error, consider contacting a professional technician or the manufacturer’s support for further assistance.
Solutions for DPC Watchdog Violation Error
11 Ways to Fix DPC Watchdog Violation Error in Windows 10/11:
1. Update Device Drivers: Update all device drivers to their latest versions to ensure compatibility with your operating system.
2. Check for Disk Errors: Run a disk repair utility to fix any errors that may be causing the DPC Watchdog Violation error.
3. Disable Overclocking: If you have overclocked your PC, disable it as it may be causing instability and triggering the error.
4. Scan for Malware: Perform a thorough malware scan to eliminate any potential threats that could be triggering the error.
5. Check Hardware Connections: Ensure all hardware components are properly connected and seated in their respective slots.
6. Update BIOS: Update your computer’s BIOS to the latest version provided by the manufacturer.
7. Remove Recently Installed Software: Uninstall any recently installed software or drivers that may be conflicting with the system.
8. Disable Fast Startup: Turn off the Fast Startup feature in Windows, as it can sometimes cause compatibility issues.
9. Adjust Power Settings: Modify your power settings to prevent the system from entering sleep mode too quickly.
10. Perform a System Restore: If the error started occurring after a recent change, use System Restore to revert your system back to a stable state.
11. Contact Customer Support: If none of the above methods resolve the issue, reach out to Microsoft Customer Support for further assistance.
Remember to restart your PC after applying each fix and monitor for any recurring DPC Watchdog Violation errors.
Disconnecting External Devices and Checking Compatibility
1. Disconnect any external devices connected to your computer, such as USB drives, printers, or external hard drives. Sometimes, conflicts with these devices can trigger the DPC Watchdog Violation error.
2. Check the compatibility of your devices with your operating system. Some older or incompatible devices may not work properly with Windows 10/11, leading to this error. Visit the manufacturer’s website to find updated drivers or compatibility information.
3. To troubleshoot the DPC Watchdog Violation error, follow these steps:
4. Press the Windows key + X and select Device Manager from the menu. Look for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark, indicating a driver issue.
5. Right-click on the device and select Update driver. Choose the option to search automatically for updated driver software.
6. If no updates are found, you may need to manually download and install the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website.
7. Additionally, you can try disabling certain devices temporarily to identify the culprit. Right-click on the device in Device Manager and select Disable device. Restart your computer and check if the error persists.
Remember, resolving the DPC Watchdog Violation error may involve trial and error. If you’re unsure about making changes, it’s always a good idea to seek professional assistance or consult the Microsoft support website for more information.
Updating Device Drivers and Firmware
1. Identify the problematic device driver(s) causing the error.
2. Visit the manufacturer’s website and download the latest drivers for the identified device(s).
3. Install the updated drivers and restart your PC.
4. Additionally, update your firmware if available.
5. Run a system scan to check for any disk errors using the built-in Repair Disk Errors method.
6. If the error persists, try disabling certain components or devices temporarily to identify the root cause.
7. Adjust the request level or IRQL DISPATCH_LEVEL value if necessary.
8. Consider using a reliable registry cleaner to fix any registry issues.
9. Ensure your operating system is up to date with the latest patches and updates.
10. If the problem still persists, contact Microsoft Support for further assistance.
Remember, keeping your device drivers and firmware updated is essential for a stable and error-free Windows experience.
Running System Checks and Troubleshooters
- Overview: Understand the importance of running system checks and troubleshooters
- Check for hardware compatibility
- Update drivers for optimal performance
- Perform a thorough virus scan using Windows Defender
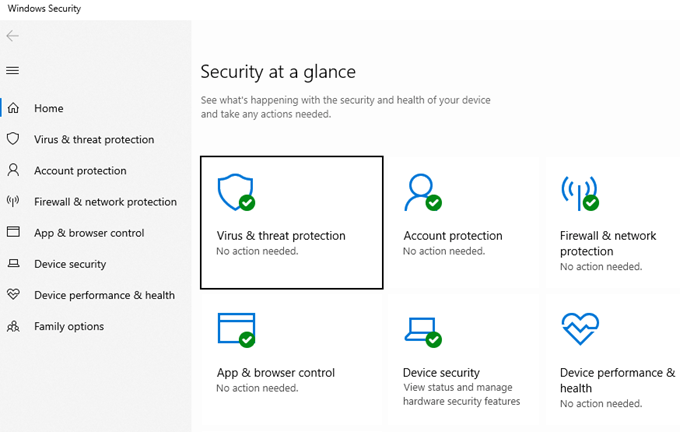
- Utilize the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool
- Run the System File Checker to fix corrupted system files
- Use the DISM tool to repair system image
- Reset your computer’s power plan settings
- Disable or update problematic drivers
- Perform a clean boot to identify software conflicts
- Seek professional assistance if issues persist
